Introduction to FTP
Adapters
While working on integration projects particularly involving
legacy systems, many times there is requirement to get a flat-file or a CSV
(Comma Separated Values) from a remote server and then process it as XML or file
using some delimiters and use this file or write the XML data into another file.
This can be achieved by Java code.
Oracle BPEL provides “FTP Adapters” to
achieve these functionalities. FTP adapter can be treated as a service which
provides following operations from a remote server.
1.Get a file from a
remote server
2.Put a file to a remote server
3.Synchronous Get or Get a
current file.
“Get” operation can be used when requirement is to poll on a
particular location or directory at particular intervals and once file with name
specified as available process it. This operation also provides an option to
delete or to achieve a processed file.
“Put” operation can be used to write
the data into a file at a particular location. The same operation provides
option to append data to an existing file and once a particular size is exceeded
create another file.
If requirement is to read data from a file at a location
which can be dynamically specified, then “Synchronous Get” operation can be
used. Following section gives the difference between “Get” operation and
“Synchronous Get” operation.
Difference between Get Adapter and Synchronous
Get Adapter
1.“Get” operation in FTP Adapter polls the given input file
periodically according to the frequency given, that is, it tries if the file is
available at given location after a specified interval waits until the given
file doesn't exist. Once file is available it starts processing it by creating
an instance of the BPEL process. Whereas “ Synchronous Get” operation in FTP
Adapter reads the file only when the instance is triggered and it does not
create the instance on its own, Neither it polls on particular
directory
2.FTP Adapter with “Get Operation” can be invoked only using
“Receive Activity” whereas for “Synchronous Get” Operation of the FTP adapter
has to be invoked using “Invoke Activity”
How to create a BPEL process using an FTP Adapter service
1. Navigate to the “Component Palette” and select “Services” option. Services
palette enlists all the services options available which can be used to invoke
another service or system using either partner links or Adapters.
2. Now drag the “FTP Adapter” and drop it in the services portion of the BPEL
process, an Adapter Configuration Wizard appears. Click next to go the next
window. In step 1, specify a desired name to the adapter and then click next to
go the next window
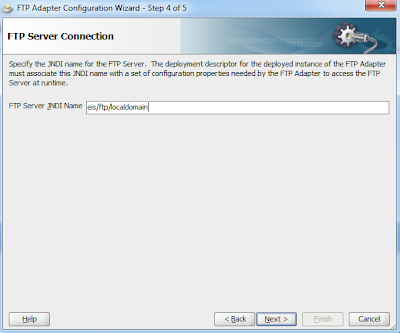
3.In Step 2, specify the JNDI name of the FTP Server.
The JNDI name of a
resource and the name of the resource reference are not the same. This approach
to naming requires mapping of the two names before deployment, but it also
decouples components from resources. Because of this decoupling, if at a later
time the component needs to access a different resource, you don't have to
change the name in the code.
(Read “How to configure the JNDI in Application
server console” at the end of
the section)
After specifying all the
required information, click next to go to the next window
4 .In the next step, select the operation as per requirement to create FTP adapter
for. Select the radio button “Get” to create an adapter to read a file and click
next to go to the next window. In FTP Adapter, an additional operation is also
supported where the user can select if the file is of ascii type or binary type.
The user can select the radio button”Ascii” if the file is of ascii type, else
select the radio button “Binary” as per the requirement.
5. In the next step, specify the path of the incoming file.
Location of the path
can be specified in two ways 1) Physical path and 2) Logical path.
Physical
path is the absolute location of the file where it is located. This specified
directory should be accessible to the server.
Logical path is the location of
the file relative to the current location of the file adapter on
server.
Default option is “Physical path”
Options either to archive
processed files or delete files after successful processing of file can be
specified using options Available.
There might be requirement to save the
files after processing the data from it. In such conditions, these files can be
achieved to by checking the box “Archive processed files” in this window. The
path of the directory where the processed files have to be saved (or archived)
after processing can be specified. Again this path can be either absolute or
logical based on the option selected earlier.
Instead, at times the files
after retrieving the data from the file need to be deleted. This can be achieved
by checking the box “Delete files after successful retrieval” in this
window.
After specifying all the required information, click next to go to
the next window.
6. In the next Step, specify the name of the file from where the data need to be
retrieved.
File names can be specified using two options, 1) File Wildcards
and 2) Regular Expressions.
“File Wildcards” allows user to specify file
having a similar naming pattern like po*.txt where * can be replaced by any
character or digit or symbol.; whereas “Regular Expressions” can be used for
normal search where in it searches for the file having similar string
pattern.
User can also specify the naming pattern of the files which
needs to be excluded (if any) from the reading operation.
“Files contain
multiple Messages” can be checked if the incoming file is expected to have more
than one message. Number of messages needs to be retrieved in batches if the
incoming file having multiple messages can also be specified. Default number is
“1”
7.Select polling frequency and minimum file age accordingly.
“Polling
frequency” is the interval after which the adapter needs to poll the file
periodically to receive the data.
“Minimum File age” is the minimum time
adapter should wait, after the file is created. In other words,”Minimum file
age” refers to the time elapsed between the file creation and next run of the
polling frequency.
Click next to go to the next window
8.The next window prompts to select a schema format for the data to be
retrieved.
Select a schema which already exists in the project (if any) or
create a new schema format using a sample data file. Click next to go to the
next window.
Click “Finish”. Click “Apply” and “OK” on the “Create partner link” window to
end the process of creating an adapter
Now create a Receive which will be listening to Incoming files from FTP.
Deploy the process to the server and the process itself creates an instance.
Check the “Flow” and “Audit” of the instance. The input file is read and
transformed to XML format. For example, if the input file contains the data
“Hello,BPEL,Process”, it will be transformed as shown below.
HappyLearning
By DeepthiReddy







No comments:
Post a Comment